Wide-gap components for power conversion
What are the advantages of integrating SiC and GaN components into power architectures?
Growing electricity consumption
The development of electrical sources and consumers means that power converters need to perform better. Innovative components such as gallium nitride (GaN), from the family of ‘large gap’ semiconductors, are positioned as solutions that meet this need for increased performance.
Electricity consumption is constantly increasing as a result of the development of :
- Electric means of transport
- Solar panel or wind farms
- Data centres and digital tools
- Electrical equipment and machinery
The efficiency of electrical systems is therefore becoming a major issue, considering the balance between :
- Performance (mainly efficiency and power density)
- Costs
Taking these criteria into account necessarily imposes constraints on the architecture of DC/DC converters and the choice of power components (active or passive).
Evolution of component technology
To improve performance, research is being carried out into the materials and technologies used for power components.
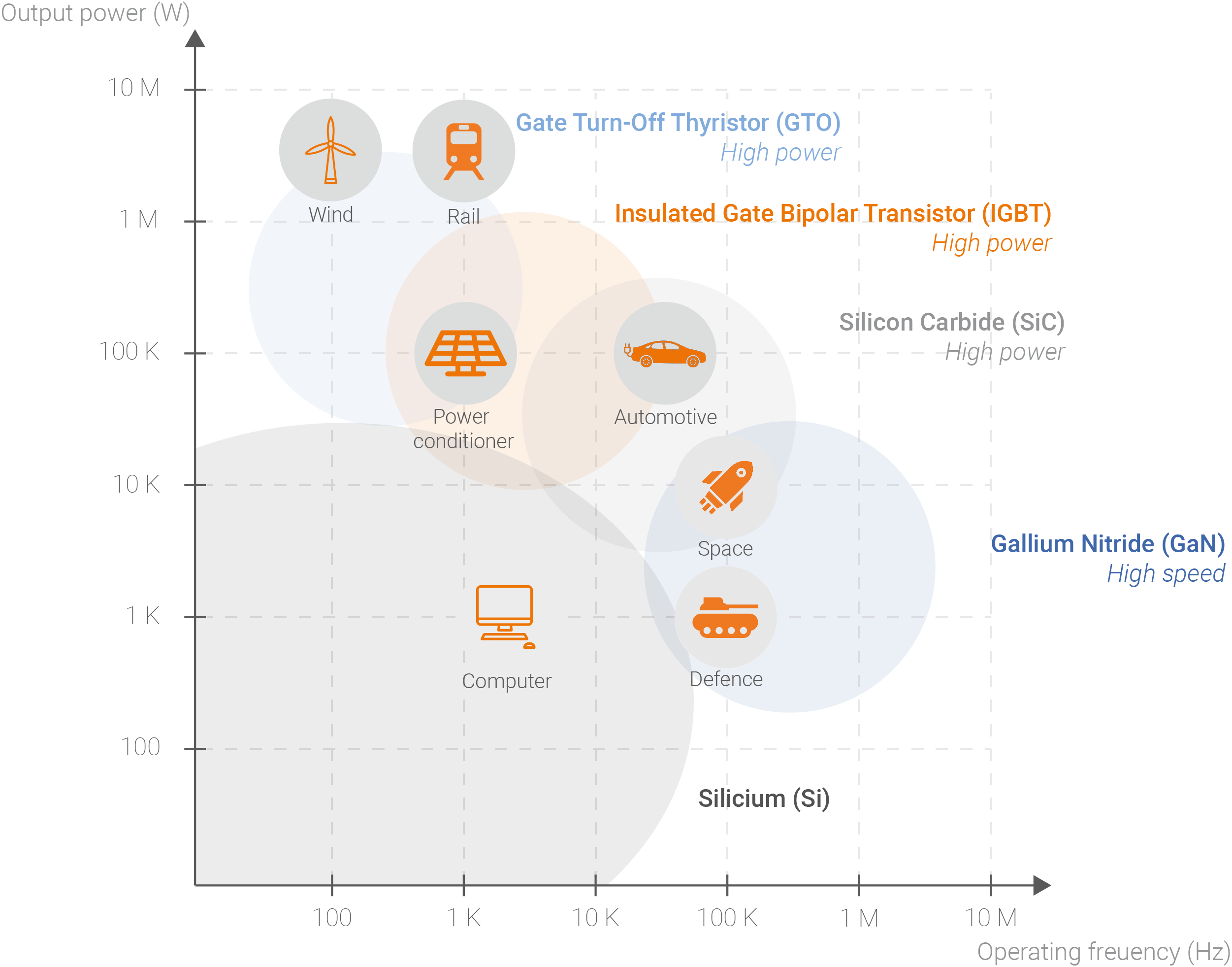
Large-gap semiconductors, such as silicon carbide (SiC) or gallium nitride (GaN), are enabling the development of power transistors with performance levels that go beyond the current MOSFET or IGBT standards, by making it possible to:
- Significantly reduce the size of DC/DC converters
- Achieve high conversion performance (efficiency)
The ability of large-gap components to switch much faster, more often and at a higher frequency than previous technologies means that the power density of energy converters can be drastically increased, both by reducing the size of the magnetics and by simplifying the cooling system.
DC DC conversion principles
DC DC energy conversion is considered to be the second stage of energy conversion:
- 1st stage – AC/DC conversion
- Power factor correction, non-isolated.
- 2nd stage – DC/DC conversion
- Adaptation of output voltage and current to the application.
- Isolation between input and output possible.
- 3rd stage (optional) – DC bus
- Smoothing of the power drawn.
The DC/DC energy conversion function is to adapt the output voltage and current to the load. Isolation may be necessary in some applications to ensure user safety.
The use of SiC and GaN components in the architecture of DC/DC converters makes it possible to develop innovative, high-performance conversion systems.
Outlook
The performance in terms of efficiency and power density offered by large-gap semiconductors is leading to their widespread use in the design of power architectures.
Emerging applications such as electric vehicles and associated chargers are encouraging the use of SiC or GaN components: bidirectional charger power is required to ensure the future role of electric vehicles in grid regulation. This regulation is achieved by injecting the energy stored in the charger into the grid, while maintaining the charge transfer properties to the electric vehicle.
This example of an application places more stringent demands on the power architecture and involves the use of SiC or GaN components for higher performance from more compact power assemblies.





